Check out my book on Amazon for everything MLOps with Databricks →
Need a Ballpark Cost Estimate? Try the Azure Data & ML Platform Cost Calculator →
Databricks Architecture Overview
A visual guide to understanding the core building blocks of the Databricks platform and how they interconnect to form a unified data lakehouse architecture.
View Interactive Version →
Architecture Visualization
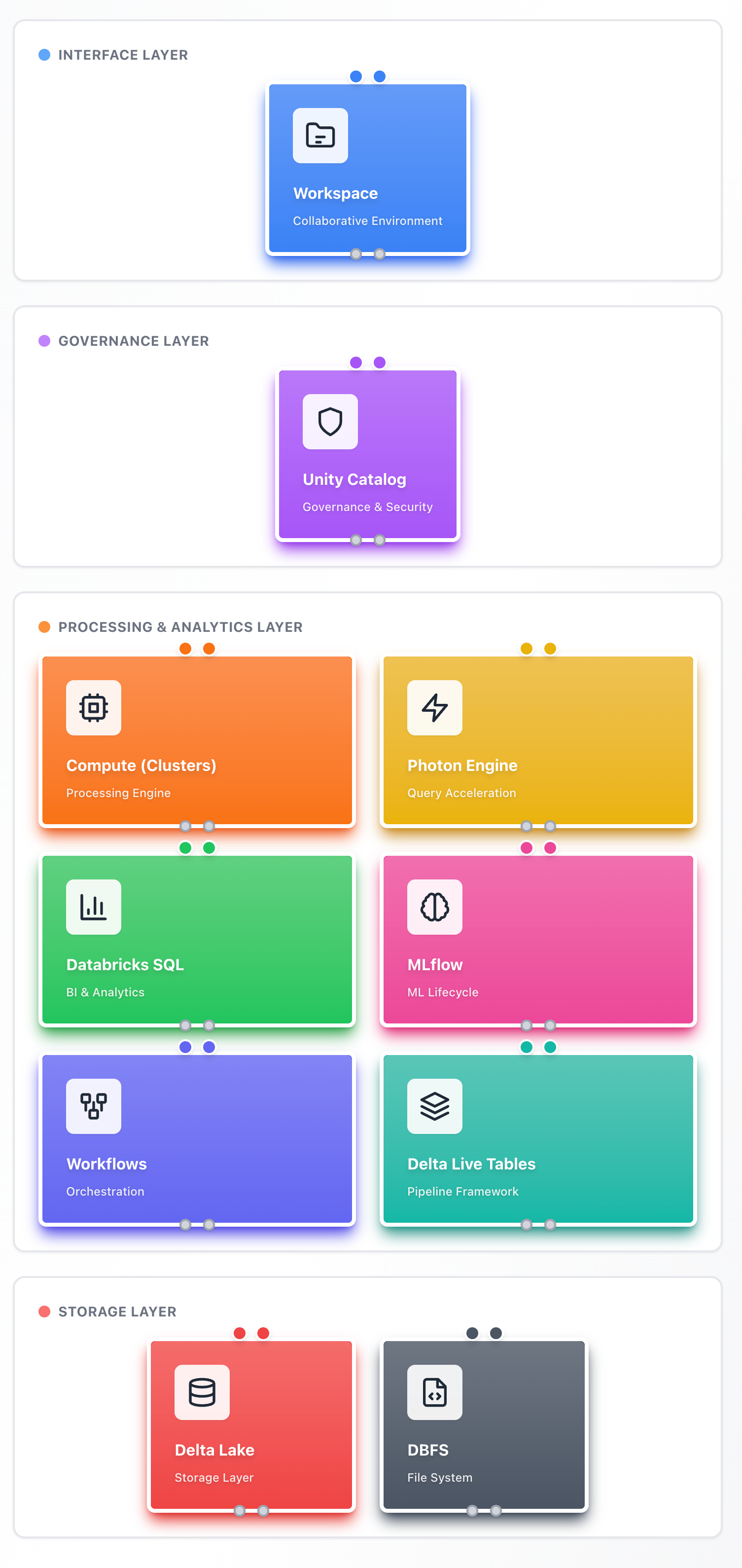
The architecture is organized into four distinct layers, each serving a specific purpose in the data lakehouse ecosystem.
Architectural Layers
Interface Layer
The Workspace provides the collaborative environment where data engineers, scientists, and analysts interact with the platform. It offers notebooks for interactive development, folder structures for organization, and integration with version control systems.
Governance Layer
Unity Catalog serves as the unified governance solution, managing access control, metadata, and data lineage across the entire organization. It provides centralized security and discoverability for all data assets.
Processing & Analytics Layer
This layer contains the core processing and analytical engines:
- Compute Clusters: Groups of virtual machines that process data at scale, supporting both interactive and automated workloads
- Photon Engine: A vectorized query engine that accelerates SQL and DataFrame operations through optimized C++ execution
- Databricks SQL: A purpose-built query interface optimized for business intelligence and analytics, with native integrations to BI tools
- MLflow: An open-source platform managing the complete machine learning lifecycle from experimentation to production deployment
- Workflows: An orchestration system that automates data pipelines and manages task dependencies
- Delta Live Tables (DLT): A declarative framework for building reliable data pipelines with built-in quality controls and error handling
Storage Layer
The foundation where data resides:
- Delta Lake: An open-source storage layer providing ACID transactions, time travel, and unified streaming/batch processing on data lakes
- Databricks File System (DBFS): An abstraction layer over cloud object storage that simplifies distributed file access across AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage
Key Data Flows
The platform’s components interact through well-defined data flows:
- Workspace → Compute Clusters: Interactive code execution and notebook-based development
- Unity Catalog → Delta Lake: Centralized governance and metadata management for all stored data
- Databricks SQL → Photon Engine: Accelerated query processing for analytical workloads
- Workflows → Delta Live Tables: Automated orchestration of declarative data pipelines
- MLflow → Compute Clusters: Machine learning model training and deployment infrastructure
- Delta Lake → DBFS: Reliable storage with versioning capabilities on distributed cloud infrastructure
Use Cases
This architecture supports multiple data and AI workloads:
- Data Engineering: Building scalable ETL/ELT pipelines with Delta Live Tables and Workflows
- Data Analytics: Running interactive queries and creating dashboards through Databricks SQL
- Data Science & ML: Developing, training, and deploying machine learning models with MLflow integration
- Data Governance: Managing access control and lineage tracking through Unity Catalog
- Real-time Processing: Handling streaming data alongside batch processing with Delta Lake
Platform Benefits
The lakehouse architecture combines the best aspects of data warehouses and data lakes:
- Unified Platform: Single platform for all data workloads, eliminating data silos
- ACID Compliance: Reliable transactions through Delta Lake’s storage format
- Performance: Accelerated queries via the Photon engine and optimized data layouts
- Governance: Centralized security and compliance through Unity Catalog
- Scalability: Cloud-native architecture that scales compute and storage independently
- Open Standards: Built on open-source technologies like Apache Spark and Delta Lake
Presented to you by mohammed-brueckner.com
